The administration of therapeutic agents or drugs directly into the peritoneal cavity, the space located between the abdominal organs and the abdominal wall, is known as intraperitoneal administration. This mode of drug delivery offers a plethora of advantages and disadvantages, and its utility in treating specific ailments hinges on multiple factors. In this exposition, we shall elucidate the rudiments of intraperitoneal administration, which encompass its benefits, biological barriers, and potential applications.
Intraperitoneal administration has been deployed in treating a wide array of diseases, particularly those that affect the abdominal cavity or organs. For instance, intraperitoneal chemotherapy has proven efficacious in treating ovarian cancer, which frequently metastasizes to the peritoneal cavity. Furthermore, intraperitoneal insulin delivery has been evaluated as a potential treatment for diabetes, as it provides a more rapid and effective response than subcutaneous injections.
In recent times, there has been a burgeoning interest in utilizing nanotechnology to augment the efficacy of intraperitoneal drug delivery. Nano-delivery products can be engineered to surmount some of the biological barriers that impede the effectiveness of conventional intraperitoneal administration, such as the limited diffusion of large molecules. Additionally, nanotechnology can be employed to target specific cells or tissues within the peritoneal cavity, thus improving the selectivity and effectiveness of the drug.
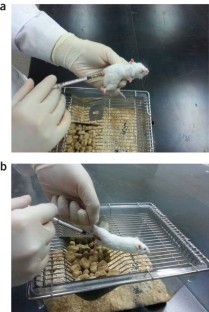 Figure 1. Intraperitoneal Administration. (Baek JM, et al.; 2015)
Figure 1. Intraperitoneal Administration. (Baek JM, et al.; 2015)
An exemplary nano-delivery product that has received approval from the FDA is Paclitaxel Protein-Bound Particles for Injectable Suspension (Abraxane), which is employed in treating ovarian and breast cancers. Abraxane is a nanoparticle-based formulation of paclitaxel. It is administered intravenously, but in some cases, it can also be given intraperitoneally. Research has evinced that intraperitoneal administration of Abraxane can furnish a more effective and well-tolerated treatment option for patients with advanced ovarian cancer.
One of the salient benefits of intraperitoneal administration is the ability to deliver drugs directly to the target site. When drugs are injected into the bloodstream, they must traverse several tissues and organs before reaching their destination, which may result in the loss of potency. Conversely, drugs that are administered intraperitoneally can interact with the target organs in the abdominal cavity by entering the peritoneal fluid. This mode of drug delivery engenders a more rapid and effective response, particularly in instances where the drug is intended to operate locally within the abdomen.
Additionally, intraperitoneal administration can deliver high concentrations of drugs to the target site, without exposing other parts of the body to excessive levels of the drug. This is particularly crucial in cases where systemic exposure to drugs may cause deleterious side effects, such as in the context of chemotherapy agents.
Intraperitoneal administration, notwithstanding its advantages, also presents several drawbacks. Foremost among these challenges is the presence of biological barriers that can limit the effectiveness of this method of drug delivery. For example, the peritoneal membrane can hinder the diffusion of large molecules, which may restrict the effectiveness of intraperitoneal chemotherapy agents. Additionally, the limited volume of the peritoneal cavity may pose an obstacle to the delivery of high volumes of drugs or large particles.
Another potential drawback of intraperitoneal administration is the requirement for specialized equipment and trained medical professionals to administer the drugs safely and effectively. This may limit the availability of this mode of drug delivery in specific settings or for particular patient populations.
CD Bioparticles is specialized in the development of drug delivery systems and customizing nanoparticles for drug delivery utilizing our core technologies. With our high-quality products and services, the efficacy of your drug delivery can be tremendously improved.
We offer custom synthesis of polymer microspheres and nanoparticles. Clients may select the material type, particle size, size distribution, color dye, fluorescent dye, and/or surface functional groups such as carboxyl or amine groups. We also encapsulate proteins, steroids, ligands, nucleic acids, and other drug molecules. Additionally, the surface coating of microspheres or nanoparticles with ligands, oligonucleotides, and other agents are available for clients to choose.
References
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.