Photo-crosslinking kits in the field of bioactive matrices are a class of tools specifically designed to cross-link bioactive materials. Such kits usually contain specific photosensitive active ingredients, which can trigger cross-linking reactions between biomolecules to form stable structures after being irradiated by light of specific wavelengths. This process has applications in areas such as biomedicine, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering.
In biomedical research, photocrosslinkable kits can be used to prepare bioactive matrices such as artificial blood vessels or cell scaffolds. By introducing photosensitive active ingredients into the matrix, researchers are able to precisely control the physical and chemical properties of the matrix. This precise control allows the matrix to release drugs under specific conditions, promote cell adhesion and proliferation, or be used to construct simulated tissue structures.
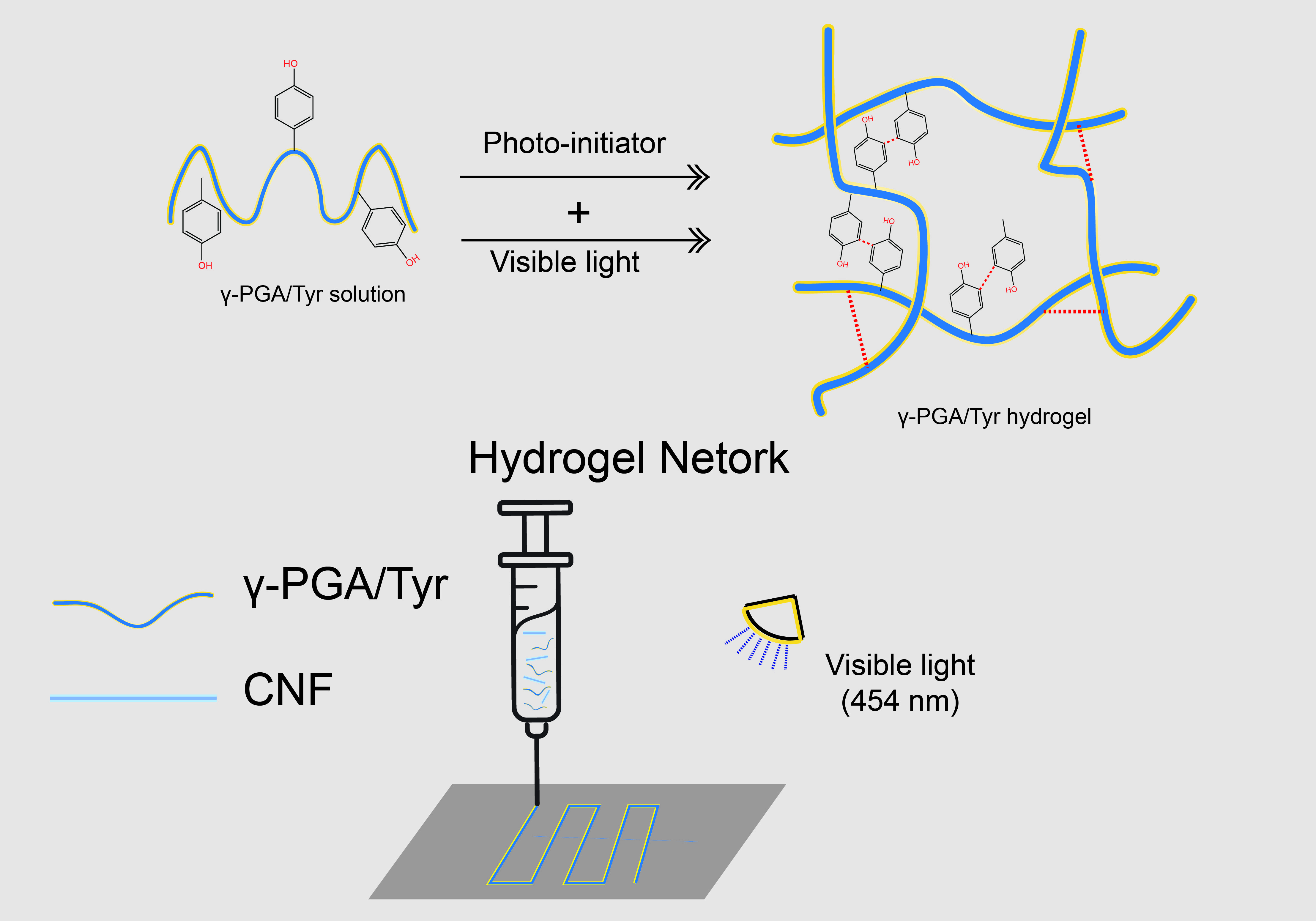
In terms of drug delivery systems, the application of photo-cross-linking kits enables drug carriers to achieve more refined release kinetics. By introducing photosensitive active ingredients into drug carriers, the release of drugs can be controlled by external light sources. This controllability helps increase the potency of drugs, reduce side effects, and enhance the targeting of treatments.
To this end, CD Bioparticles provides photocrosslinkable kits to help solve the following challenges.
The challenges you might meet:
- Open biomaterials require precise control of the physical and chemical properties of the bioactive matrix, including surface properties, release kinetics, and biocompatibility.
- Lack of drug carriers with precise drug release capabilities
- The biomedical devices or tissue engineering materials developed have strong immune rejection
- In research, it is difficult to introduce specific bioactive molecules, such as proteins, peptides or growth factors, into biological materials conveniently and quickly.
Photocrosslinkable kits key features:
Photocrosslinkable kits key benefits:
- Precise spatial and temporal control: Photocrosslinkable kits provide precise control of the cross-linking process in bioactive matrices. By adjusting the spatial distribution and time parameters of illumination, researchers can achieve localization, directional modification of the substrate, and dynamic regulation of biological responses.
- Controlled release of bioactive substances: In drug delivery and biomedical applications, photocrosslinkable kits allow controlled release of drugs or bioactive molecules. This controlled release helps improve therapeutic effects, reduce adverse reactions, and release the desired bioactive substances within a specific period of time.
- Improved biocompatibility: The use of photocrosslinkable kits can improve the biocompatibility of bioactive matrices. By introducing specific bioactive molecules or functional groups, the matrix can better interact with surrounding biological tissues and reduce immune rejection.
- Designed for Versatility: Photocrosslinkable kits can be used to introduce a variety of biomolecules, such as cell adhesion proteins, growth factors or signaling molecules, into bioactive matrices. This allows the matrix to mimic the complex microenvironment of biological tissues and support specific cell activities and tissue regeneration.
- Reversible cross-linking: Some photocrosslinkable kits are designed to be reversible, so that the cross-linking reaction can be unraveled, thereby restoring the free state of the matrix. This facilitates modification or adjustment of the bioactive matrix when required.
- Highly selective: Photo-crosslinking technology usually exhibits a high degree of selectivity and only cross-links with specific functional groups or biomolecules. This helps reduce non-specific cross-linking and improves the accuracy of experimental results.
Photocrosslinkable kits application candidates:
- Biomedical material design: For the preparation of bioactive matrices, such as artificial blood vessels, cell scaffolds and bioceramics, to improve biocompatibility and control the release characteristics of materials.
- Drug delivery system: used to design carriers for controlled release of drugs. By regulating the photo-cross-linking process, the directional release of drugs and improved therapeutic effects can be achieved.
- Tissue engineering: Used to construct biocompatible and functional tissue engineering scaffolds to promote cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation.
- Research on cell-material interaction: Used to study the interaction between cells and biological materials, to understand the impact of biological materials on cell behavior, and the response of cells to biological materials.
- Protein and Nucleic Acid Research: Used to capture and study interactions between proteins and their ligands, substrates, or DNA/RNA to gain a deeper understanding of biomolecule structure and function.
- Biosensor Development: Used to build biosensors with high sensitivity and specificity to detect changes in biomarkers or molecules.
- Microfluidic chip technology: Used in biological reaction chambers on microfluidic chips to control and monitor biological processes on a microscopic scale.
- Medical imaging: Used to improve the characteristics of medical imaging reagents, such as increasing contrast and adjusting release speed, to better meet the needs of medical imaging.
- Biomaterial surface modification: used to improve the characteristics of biomaterial surfaces, such as improving cell adhesion and reducing thrombosis, to improve the performance of medical devices.


