CD Bioparticles’ products with customized delivery strategies, precise designs and modifications of drugs or drug-contained cargos, and advanced technical platforms can help you to solve:
The challenges you might meet:
- Limited options of drug-loaded or non-loading liposomes for positive control and negative control of your drug delivery tests or exosome studies
- Complicated formulation of lipid composition and ratio to prepare artificial cell models
- Hard to incorporate active biomolecules, such as peptide, antibody, protein, nucleic acid, and polysaccharide on the surface of the liposomes
- Limited options for tracking and detection of fusion, pore forming, and cell uptake (e.g. macrophage) experiments
- Hard to track and image the distribution of the liposomes
- Tedious chemical synthesis, formulation, and purifications
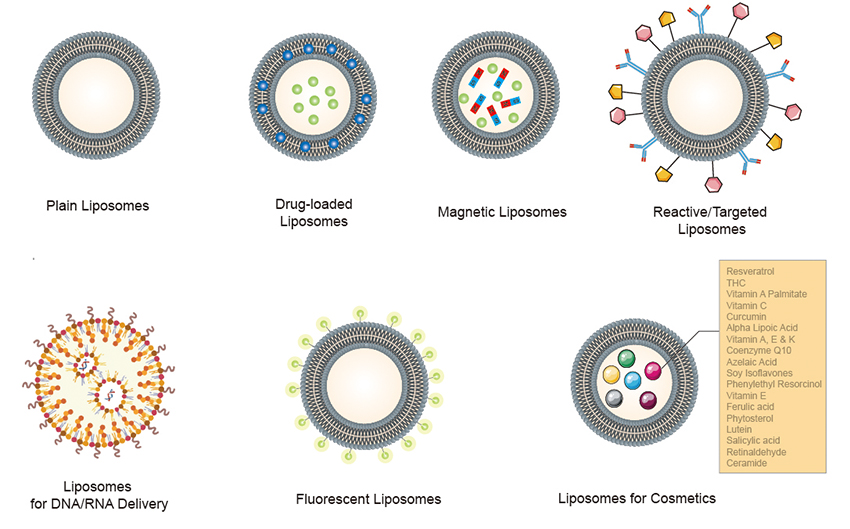 Figure 1. Schematic representation of the classification of different liposomes.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the classification of different liposomes.
Plain Liposomes Key features:
DOTAP-based Cationic Liposomes
Total Lipid Liposomes from Natural Lipid Extracts
Phosphatidylserine (PS) Liposomes
Cardiolipin Lipids (CL) Liposomes
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) Liposomes
Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) Liposomes
Folate Liposomes
Cyanur Liposomes
Succinyl Liposomes
Glutaryl Liposomes
Amine Liposomes
Carboxylic Acid Liposomes
Metal Chelating Liposomes: Ni Reactive Liposomes:
Biotinylated Liposomes
Dodecanyl Liposomes:
Azide Liposomes
DBCO Liposomes
PDP Liposomes: Sulfhydryl Reactive Liposomes
Fluorescent Plain Liposomes
Fluorescent Reactive Liposomes
Fluorescent Drug Loaded Liposomes
Fluorescent Liposomes for DNA/RNA Delivery
Wide coverage of the Fluorescent options
Liposomal ATP
Liposomal DOTA
Liposomal TPT
Liposomal Clodronate
Liposomal Doxorubicin
Liposomal ALD
Resveratrol
THC
Vitamin A Palmitate
Vitamin C
Curcumin
Alpha Lipoic Acid
Vitamin A, E & K
Coenzyme Q10
Azelaic Acid
Soy Isoflavones
Phenylethyl Resorcinol
Vitamin E
Ferulic acid
Phytosterol
Lutein
Salicylic acid
Retinaldehyde
Ceramide
-
API loaded Liposomes
Food additives
- Vitamine A liposomes
- Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) liposomes
- Curcumin liposomes
- AEK liposomes
- HK20 liposomes
- Ferulic Acid liposomes
- Asta liposomes
- Q10 liposomes
- Resveratrol liposomes
- Lutein liposomes
- Vitamine E liposomes
- ISO (Estradiol) liposomes
- Vitamine C liposomes
Cosmetic additives
- 4-Hexylresorcinol liposomes
- Retinol liposomes
- Idebenone liposomes
- r-Retinoate liposomes
- Liposomal o-Cymen-5-OL
- Liposomal Asta
- Liposomal Resveratrol
- Liposomal THC
- Liposomal Vitas
- Liposomal Pterostilbene
- Liposomal Gallic acid
- Natural Soluble Yeast Beta-Glucan
- Phytosterol liposomes
- Azelaic liposomes
- Liposomal 377
- 5-amino-4-oxovaleric acid
- Galla Rhois Gallnut Extract Nanoemulsion
- Salicylic Acid liposomes
- Anti-acne concentrates liposomes
DDAB Liposomes for DNA/RNA Delivery
GL-67 Liposomes for DNA/RNA Delivery
DOTMA Liposomes for DNA/RNA Delivery
DOTAP Liposomes for DNA/RNA Delivery
DODAP Liposomes for DNA/RNA Delivery
DC-Cholesterol Liposomes for DNA/RNA Delivery
Plain Liposomes Key benefits:
- Wide coverage of the functional liposomes
- Cell-membrane mimic liposomes
- Multi-functional-group useful for further conjugation and crosslinking, good for further conjugation, labeling, targeting
- Wide coverage of fluorescent lipophilic tracer for tracking and detection of the liposomes
- Precise control of the fluorophore substitution, well-control of the intensity-concentration dependence
- Optimized liposome composition improving transfection efficiency and stability
- Fluorescent cationic liposome useful tracking and imaging of the transfection
- Post PEGylation useful for optimizing the PEG ratio
- Pre-loaded API liposomes useful for various of formulations and studies
- Ready-to-use
Plain Liposomes Application candidates:
- Control formulations for many different types of drug encapsulated liposome formulations.
- Artificial cell models
- Charged liposomes useful in many different types of blood complement studies
- Tracking and imaging of the transfection
- DNA/RNA delivery
- Fusion experiments of two separate membranes.
- Tracking and detection of cell uptake (e.g. macrophage)
- Long circulation applications
- Experiments that involve pore formation and disruption of the membrane, to study pore formation or disruption by external factors such as detergents, peptides, etc.
 Figure 1. Schematic representation of the classification of different liposomes.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the classification of different liposomes.