CD Bioparticles offers custom services to characterize drug stability. For recent years, our experienced scientists have been dedicating ourselves to helping every custom to measure drug stability when bioparticle formulation is applied.
The nanoparticle stability is a major consideration for nanoparticles production and administration steps: from process to storage and delivery. A stable pharmaceutical dosage form maintains its physical integrity and does not adversely influence the chemical integrity of the active ingredient during its life. Researchers are attempting to deliver low and high molecular weight drugs in a variety of polymer matrices and liposome suspensions. The successful introduction of dosage forms depends upon a well-defined stability study. In designing a stability study, physical, chemical and microbial parameters must be considered and evaluated. A stability study must include a section for product characterization and another section concerning the product stability during storage.
Bioparticle size and morphology analysis has been found to have a profound effect on the stability studies of bioparticle, therefore it becomes crucial to measure particle size and morphology analysis. Different types of bioparticles might have different size characters, and also size monitoring before and after drug encapsulation is a prerequisite step of quality control for a successful formation development in drug delivery. In addition, the size of some bioparticles will change upon their storage, such as liposomes. All prepared liposomes are supposed to be heterogeneous in size, the average size distribution of liposomes changes upon their storage. Liposomes tend to fuse and grow into bigger vesicles, which is a thermodynamically more favorable state. Fusion and breakage of liposomes on storage also pose a critical problem leading to drug leakage from the vesicles. Therefore, visual appearance and size distribution are important parameters to evaluate physical stability.
The methods of bioparticle size and morphology analysis
Besides the visualization of bioparticles, the BET absorption could also be used to detect bioparticle self-association. The BET adsorption applies to systems of multilayer adsorption and usually utilizes probing gases that do not chemically react with material surfaces as adsorbates to quantify specific surface area. Nitrogen is the most commonly employed gaseous adsorbate for surface probing by BET methods. For this reason, standard BET analysis is most often conducted at the boiling temperature of N2 (77 K). BET platform is an alternative method to study the degree of nanoparticles self-association which can be calculated from BET data shown below.
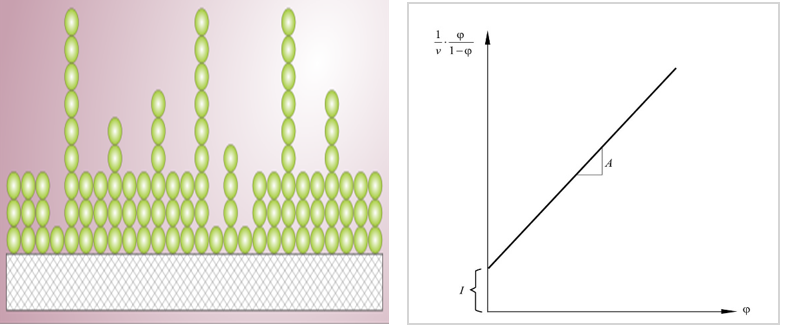
Figure 1. BET model of multilayer adsorption and BET plot.
The zeta potential is a very good index of the interaction magnitude between colloidal particles. Measurements of zeta potential are commonly used to predict the stability of colloidal systems. If all the particles in suspension have a large negative or positive zeta potential then they will tend to repel each other and there will be no tendency to aggregation. Otherwise, there will be no force to prevent the particles from aggregating. Therefore, the zeta potential is an important parameter for the stability of biological particles.
The methods of zeta potential analysis
A change in the rate of release of the active substances also marks a change in the stability of the drug carriers. In vitro drug release can be performed using the dialysis tube diffusion technique. The extra-membrane drug concentration was measured at a fixed time point to obtain a drug release rate. Further, data related to the stability of biological particles is obtained.
The methods of the release rate of active ingredient analysis
Release rate could be affected by the following factors:
CD Bioparticles offers a full set of service for bioparticle stability analysis. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly send us an inquiry.
Quotations and Ordering

References:
1. A. Laouini, et al. Preparation, Characterization and applications of liposomes: state of the art. Colloid Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 1(2): 147–168.
2. Rödelsperger K., et al. Fibre years, pulmonary asbestos burden and asbestosis. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. 2002, 205, 245-248.
3. Mojca P., et al. Stability of nanoparticle suspensions in different biologically relevant Media. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures. 2012, 7(4): 1389-1400.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.