CD Bioparticles offers a comprehensive platform for the design, synthesis, ligand conjugation, modification, and evaluation of drug delivery carriers based on nano-carriers for tumor targeting. Our professional carrier construction, combined with in vivo and in vitro analysis and characterization, enables us to provide a range of nanoparticles and services that meet the unique needs of tumor targeted drug delivery systems.
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a complex ecosystem consisting of not only tumor cells but also vasculature, stroma, infiltrating immune cells, fibroblasts, and other noncellular tissues. The characteristics of the tumor microenvironment include hypoxia, acidosis, high interstitial fluid pressure, and so on. These features limit the growth and development of tumor cells and provide protection against therapy and immune attack. However, these characteristics also provide selectivity for targeted tumor therapy.
The physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles, such as size, shape, and surface charge, can be tailored to perform controlled release of payloads, passively accumulate in the tumor through enhanced permeability and retention effect, or actively target the tumor. Nanoparticles combining physical and biological technologies have been used for delivering vaccine adjuvants, cytokines, and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Currently, there are several types of nanomaterials that are used for targeting tumors, including: Liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, dendrimers, carbon nanotubes, gold nanoparticles, iron oxide nanoparticles, viral vectors, bacterial vectors and cell vectors etc.
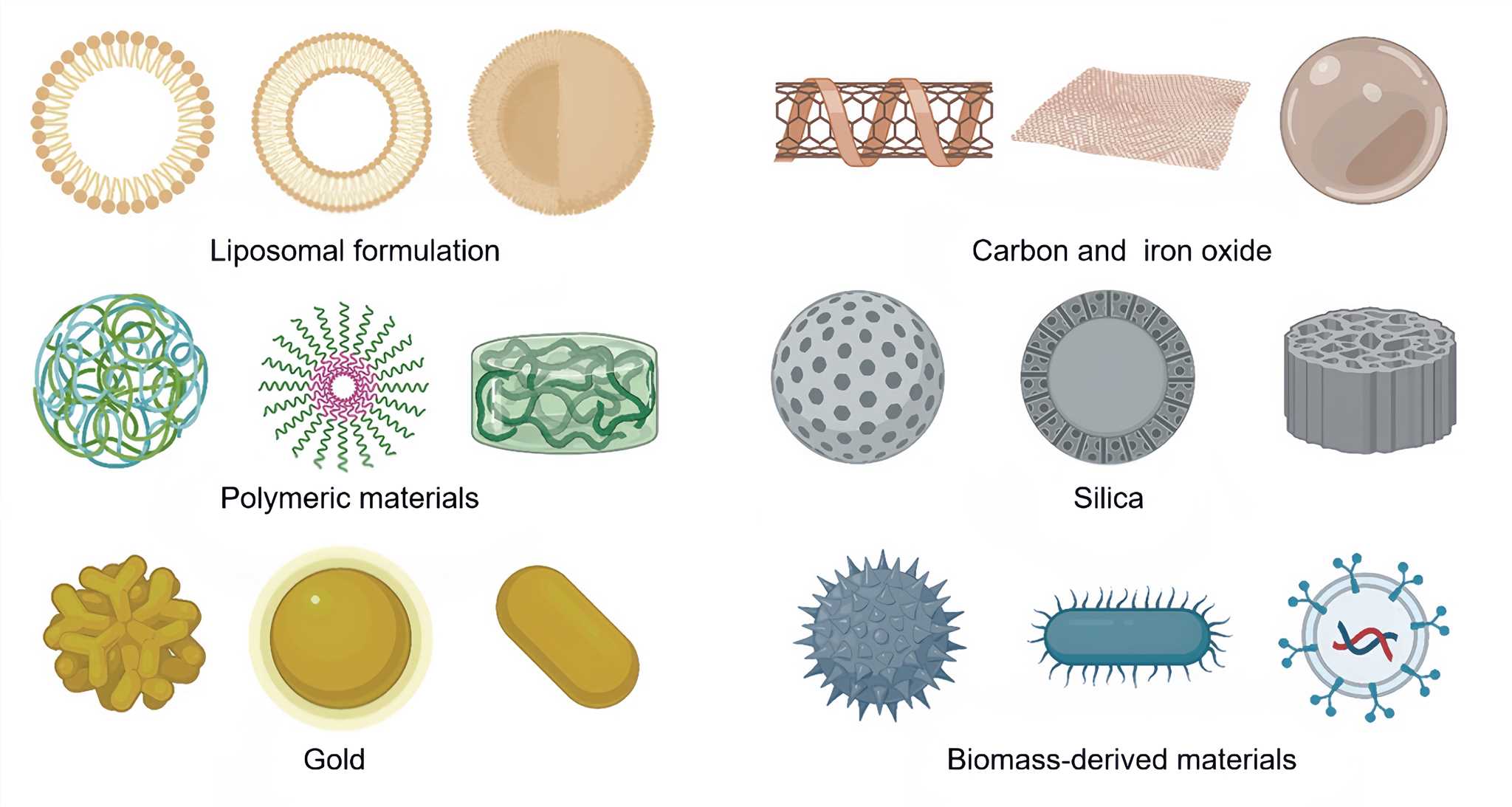 Figure 1. Various non-invasive strategies for tumor targeting[2]
Figure 1. Various non-invasive strategies for tumor targeting[2]
Tumor-targeted drug delivery systems can effectively reduce the toxic side effects of traditional anti-tumor drugs. The following are the characteristics of the drug delivery system for tumor targeting:
There are many drug delivery systems that are currently playing a vital role in the treatment of tumors. The examples provided in the table below serve as a simple reference to help understand these systems.
Table 1. List of medicines which have be approved by FDA or EMA
| Product name | Carrier | Ingredient active | Therapeutic indication | Date of Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eligard® (Tolmar) |
Polymer (PLGH (poly (dl-lactideco glycolide) |
Leuprolide acetate | Prostate cancer | FDA (2002) |
| Mepact (mifamurtide, L-MTP-PE) | Liposomes | Muramyl tripeptide phosphatidyl ethanolamine | Nonmetastatic resectable osteosarcoma | EMA (2004) |
| Lipoplatin® | Pegylated liposomes | Cisplatin | Non-small lung cancer and pancreatic, gastric, breast, head and neck cancers | EMA (2009) |
| Nanotherm® (MagForce) | Aminosilane-coated Iron nanoparticles | Iron oxide | Brain tumor | FDA (2010) |
| Marqibo | LNP | Vincristine | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | FDA (2012) |
| Abraxane® (Celgene) |
Albumin-bound paclitaxel nanoparticles |
Paclitaxel (ABI-007) | Breast cancer; non-small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer | FDA (2005;2012;2013) |
| Onivyde® (Merrimack) | Liposomes | Irinotecan | Pancreatic cancer | FDA (2015) |
| Onpattro® (Patisiran) | LNP | SiRNA versus transthyretin | Transthyretin-induced amyloidosis | FDA (2017), EMA (2018) |
|
Apealea® (Oasmia Pharmaceutical AB) |
Polymer-based Nanoparticles | Paclitaxel |
Ovarian cancer, peritoneal cancer, fallopian tube cancer |
EMA (2018) |
Table 2. Targeting Ligands Used in Preclinical Studies for Tumor Targeting
| Ligand Type | Examples | Ligand Type | Examples | Ligand Type | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody and fragments | Anti-SSTR2 mAb | Proteins or ligands | ITGβ4 or IL3 |
Nucleic acid-based ligands |
AS1411 aptamer |
| Anti-EGFR nanobodies | Biotin and avidin | Sgc8 aptamer | |||
| In-tandem scFvs against CD3 and HER2 | Peptides | GE11 peptide | Small molecules | Folic acid | |
| Anti-EGFR CAR, anti-HER2 CAR |
R8 peptide, K4 peptide |
Sialic acid |

References
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.