CD Bioparticles has an advanced and customizable drug delivery platform to help you solve all the problems of drug delivery in one stop. We provide high-quality cleavable linkers for carrier and drug conjugation, which can help you solve:
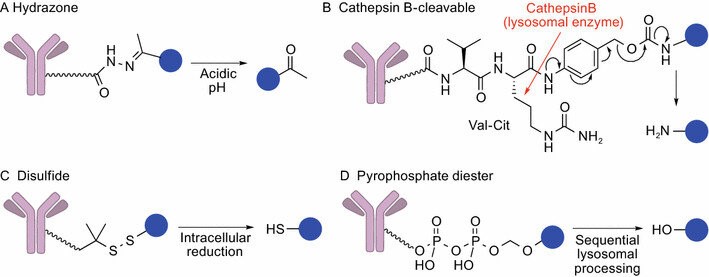 Figure 1. Cleavable linkers. (Tsuchikama K, et al.; 2018)
Figure 1. Cleavable linkers. (Tsuchikama K, et al.; 2018)
The challenges you might meet:
- The drug delivery system cannot control release, has strong off-target effects, and has poor therapeutic effects.
- Contains drugs that are susceptible to degradation when exposed to blood or the surrounding environment
- Drugs can cause side effects as they are distributed throughout the body
- The contained drug has limited solubility, making formulating it for intravenous administration challenging
- Drugs have shorter circulation time
- In combination therapy, drugs need to be released sequentially or coordinatedly at the target site
- Drugs developed are susceptible to drug resistance
Cleavable Linkers Key features:
- PC Cleavable Linkers
- PC Alkyne-PEG4-NHS carbonate ester
- PC Azido-PEG11-NHS carbonate ester
- PC Biotin-PEG3-alkyne
- PC Biotin-PEG3-azide
- PC Biotin-PEG3-NHS carbonate ester
- PC DBCO-PEG3-biotin
- PC Mal-NHS carbonate ester
- PC Methyltetrazine-PEG4-NHS carbonate ester
- PC SPDP-NHS carbonate ester
- PC-Biotin-PEG4-NHS carbonate
- PC-Biotin-PEG4-PEG3-azide
- PC-Biotin-PEG4-PEG4-alkyne
- Dde Cleavable Linkers
- Dde Biotin-PEG4-alkyne
- Dde Biotin-PEG4-azide
- Dde Biotin-PEG4-DBCO
- Dde Biotin-PEG4-Picolyl azide
- β-Glucuronide Linkers
- (2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-methyl-6-(2-(3-((Fmoc-amino) propanamido)-4-PNP-3,4,5-triacetoxy-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-carboxylate
- 4-Formyl-2-nitrophenyl-β-D-Glucopyranosiduronic Acid Methyl Ester 2,3,4-Triacetate
- β-D-Glucopyranosiduronic acid, 2-amino-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl, methyl ester, 2,3,4-triacetate
- β-D-tetraacetylgalactopyranoside-PEG2-azide
- β-D-triacetylglucopyranosiduronyl methyl ester-phenol-β-Alanine
- β-tetraacetylglucopyranoside-glycerol
- β-tetraacetylglucopyranoside-glycol
- -S-S- Cleavable Linkers
- 2-hydroxyethyl disulfide mono-Tosylate
- Acid-PEG2-SS-PEG2-acid
- Acid-PEG3-SS-PEG3-acid
- Acid-PEG4-S-S-PEG4-acid
- Acid-PEG6-SS-PEG6-acid
- Amino-SS-PEG12-acid
- Aminoethyl-SS-ethylalcohol
- Aminoethyl-SS-ethylamine
- Aminoethyl-SS-propionic acid
- Azido-PEG3-SS-PEG3-azide
- Azido-SS-PEG2-acid
- Azidoethyl-PEG2-t-Butyl ester
- Azidoethyl-SS-ethylalcohol
- Azidoethyl-SS-ethylamine
- Azidoethyl-SS-ethylazide
- Azidoethyl-SS-propionic acid
- Azidoethyl-SS-propionic NHS ester
- Biotin-bisamido-SS-NHS
- Bis-Tos-(2-hydroxyethyl disulfide)
- Boc-aminooxy-ethyl-SS-propanol
- Boc-NH-ethyl-SS-propionic acid
- Fmoc-NH-ethyl-SS-propionic acid
- Fmoc-NH-ethyl-SS-propionic NHS ester
- Hydroxy-PEG3-SS-PEG3-alcohol
- m-PEG6-SS-PEG6-methyl
- Mal-NH-ethyl-SS-propionic acid
- NThiol-SS-biotin
- Propargyl-PEG1-SS-alcohol
- Propargyl-PEG1-SS-PEG1-acid
- Propargyl-PEG1-SS-PEG1-PFP ester
- Propargyl-PEG1-SS-PEG1-propargyl
- Propargyl-PEG1-SS-PEG1-t-butyl ester
- Sulfo-NThiol-SS-biotin
- t-Boc-Cystamine
- THP-SS-alcohol
- THP-SS-PEG1-t-butyl ester
- THP-SS-PEG1-Tos
- Cleavable Peptide Linkers
- Diazo Biotin Cleavable Linkers
- Diazo Biotin-PEG3-alkyne
- Diazo Biotin-PEG3-azide
- Diazo Biotin-PEG3-DBCO
Cleavable Linkers Key benefits:
- Low immunogenicity
- Intracellular drug release rate is higher
- Interact with or to manipulate the biological target
- Rupture resistance and specific cracking conditions
- The structure does not affect the activity of other proteases
- High tumor affinity and specificity
- Increase the hydrophilicity of the loaded drugs
- High bioavailability and biocompatibility
- Mild cracking conditions
- Suitable for in vitro and in vivo experiments
- Ready-to-use
Cleavable Linkers Application candidates:
- As an on-off switch for the release of antitumor drugs
- As a crosslinking agent to improve the stability of nanoparticles
- As a linking agent to construct nano-drug carrier
- As transfection vectors to deliver DNA and siRNA
- Construction and application of peptide/protein-conjugated drugs
- Tags for MS analysis or purification
- Study on metabolism of glucuronidation and drug metabolism in vivo
- Investigate the role of linker chemistry in enhancing drug efficacy, increasing cycle time and reducing toxicity
- Fluorescent probes for diagnostic tools, proteomic analysis or cell imaging
- Protein–protein interactions
- Activity-based protein profiling
- Elucidation of drug targets and their binding sites
- Study on covalent metabolite interactions
Reference
- Tsuchikama K, An Z. Antibody-drug conjugates: recent advances in conjugation and linker chemistries. Protein Cell. 2018, 9(1):33-46.
 Figure 1. Cleavable linkers. (Tsuchikama K, et al.; 2018)
Figure 1. Cleavable linkers. (Tsuchikama K, et al.; 2018)