Using nanoparticles for the delivery of small molecules in anticancer therapy is a rapidly growing area of research. Nanoparticles can be used in targeted drug delivery to improve the aqueous solubility of poorly soluble drugs and the bioavailability of drugs and thus are widely applied in therapeutic uses. CD Bioparticles is experienced in providing small molecule drug carriers such as polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, viral-like nanoparticles for your need.
Drug delivery systems that deliver the small molecule drugs in a manner that meets the therapeutic need of the patient while eliciting fewer adverse effects are becoming increasingly common. In recent years, the development of therapeutic nanoparticles for the delivery of small molecule anticancer agents has received great attention from the medical research community. Many small molecules have been employed for different medical therapeutic uses over the years with great success. From the most dreaded diseases like cancer, diabetes, epilepsy, obesity to more humane ailments of cough, fever, cold amongst others.
Small molecule drugs are low but variably specific (predominantly) organic substances with well-defined structures and molecular weight less than 900 Daltons that help regulate biological processes mainly by metabolic degradation. The small molecules can reach almost any desired destination in the body because of their tiny size. Their small structure and chemical composition often also help them to easily penetrate cell membranes. Several small molecule drugs including paclitaxel, doxorubicin, and 5-fluorouracil have been successfully formulated using nanotechnology.
The advantages of using nanoparticles for delivering small molecule drugs are displayed as follows:
Owing to their flexible characteristics, nanoparticles can be fabricated from biodegradable, absorbable and biocompatible polymeric materials. Therapeutic nanoparticles can be formulated with several materials such as lipids (liposomes), polymers (macromolecules, micelles or dendrimers) and viruses (viral-like nanoparticles) with distinct characteristics.
More and more small molecule medications are using this technology for in vivo delivery as a result of the advancement of nanoparticle delivery research, including:
Paclitaxel: A chemotherapy medication called paclitaxel is used to treat many cancers. To increase its solubility and enable more precise delivery to tumor cells, it is frequently encased in nanoparticles.
Doxorubicin: Another chemotherapeutic agent used to treat cancer. Its stability, toxicity, and accumulation in tumor tissues are improved via nanoparticle delivery techniques.
Methotrexate: It is a drug used to treat autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis as well as cancer. Nanoparticle compositions can lessen adverse effects while increasing bioavailability.
Curcumin: An organic substance present in turmeric that has potential medicinal benefits, such as anti-inflammatory and anticancer characteristics. Curcumin's stability, solubility, and targeted delivery can all be improved by encapsulating it in nanoparticles.
Ibuprofen: A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication (NSAID) that's frequently used to treat inflammation and relieve discomfort. When delivered specifically to inflammatory areas, nanoparticles can increase a substance's bioavailability.
Tamoxifen: Tamoxifen can be encapsulated in nanoparticles to increase its solubility, boost cellular uptake, and improve therapeutic efficacy when used to treat hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.
Rapamycin: An immunosuppressant used in the treatment of some malignancies and during organ transplantation. Systems for delivering nanoparticles can enhance a drug's anticancer effects, decrease toxicity, and improve pharmacokinetics.
Cisplatin: A chemotherapeutic agent used to treat several cancers, such as lung, ovarian, and testicular cancer. Formulations using nanoparticles can increase its accumulation in tumor tissues, lessen its toxicity to the kidneys, and improve its stability.
Methotrexate: A medicine that is antimetabolite and antifolate and is used to treat autoimmune illnesses and chemotherapy for cancer. Systems for delivering nanoparticles can increase a substance's bioavailability, lengthen its duration in circulation, and boost therapeutic effectiveness.
Etoposide: A topoisomerase inhibitor that is used to treat many malignancies, including testicular and lung cancer. Its solubility, stability, and targeted delivery to tumor cells can all be improved by nanoparticles.
It's crucial to remember that the precise nanoparticle delivery methods and formulations can change depending on the intended use, the condition being targeted, and the state of the science.
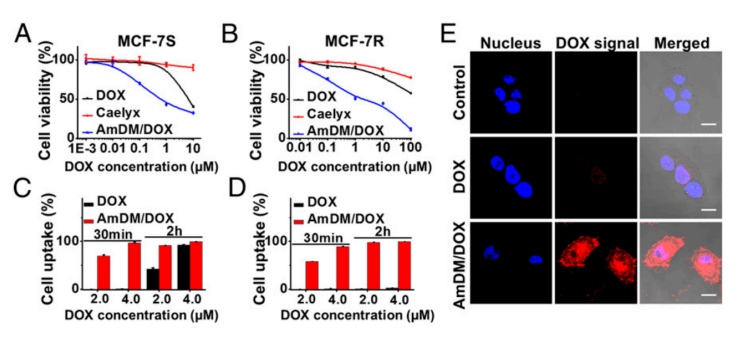
Figure 1. Dox loaded nanomicelles (AmDM) show enhanced antiproliferation efficiency and effective cellular uptake. (Wei, T., et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 201418494.)
CD Bioparticles is specialized in the development of drug delivery systems and customizing nanoparticles for small molecule drug delivery utilizing our core technologies. With our high-quality products and services, the efficacy of your small molecule drug delivery can be tremendously improved.
We are experienced small molecule drugs supplier that helps for small drug molecule development. We can help you better understand the properties of small molecule drugs and then chose an appropriate carrier for your need. And we are proficient in designing and synthesizing polymeric nanoparticles, nanocapsules, liposomes, micelles, dendrimers and other nanoparticles for small molecule drug delivery. Carrier properties such as molecular weight, surface charges and charge density, solubility, and hydrophobicity could be designed and engineered at your will; as well as the addition of desired chemical groups or targeting moieties for further functionalization.
References:
1. Nwibo, D. D., Levi, C. A., Nwibo, M. I. Small molecule drugs; down but not out: a future for medical research and therapeutics. IOSR-JDMS, 2015, 14, 70-77.
2. Chen, Z. Small-molecule delivery by nanoparticles for anticancer therapy. Trends in molecular medicine, 2010, 16(12), 594-602.
3. Kidane, A., Bhatt, P. P. Recent advances in small molecule drug delivery. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, 2005, 9(4), 347-351.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.