Drug Targeting Strategy
Related Sections-Services
CD Bioparticles' services with customized delivery strategies, precise designs and modifications of drugs or drug-contained cargos, and advanced technical platforms can help you to solve:
The challenges you might meet:
-
Fast clearance/ fast degradation/ short circulation time of the drugs
-
Unwanted immunogenicity
-
The requirements for further processing the drugs, such as dispersing in, blending in or coating on another phase
-
Low cell-permeability of the drugs
-
Low specificity of the targeting
-
High dosage required for treatment
-
High side-effect of the toxic chemotherapeutic agents
-
Tedious searching and conjugation of receptor-targeting-moieties
-
Low stability or low activity of the drugs after various barriers within a biological system
-
Highly frequent feeding of the drugs
-
The requirements of sustained release, pulse release, and delayed release
-
The requirements of the delivery at specific period, specific location, and specific dosage
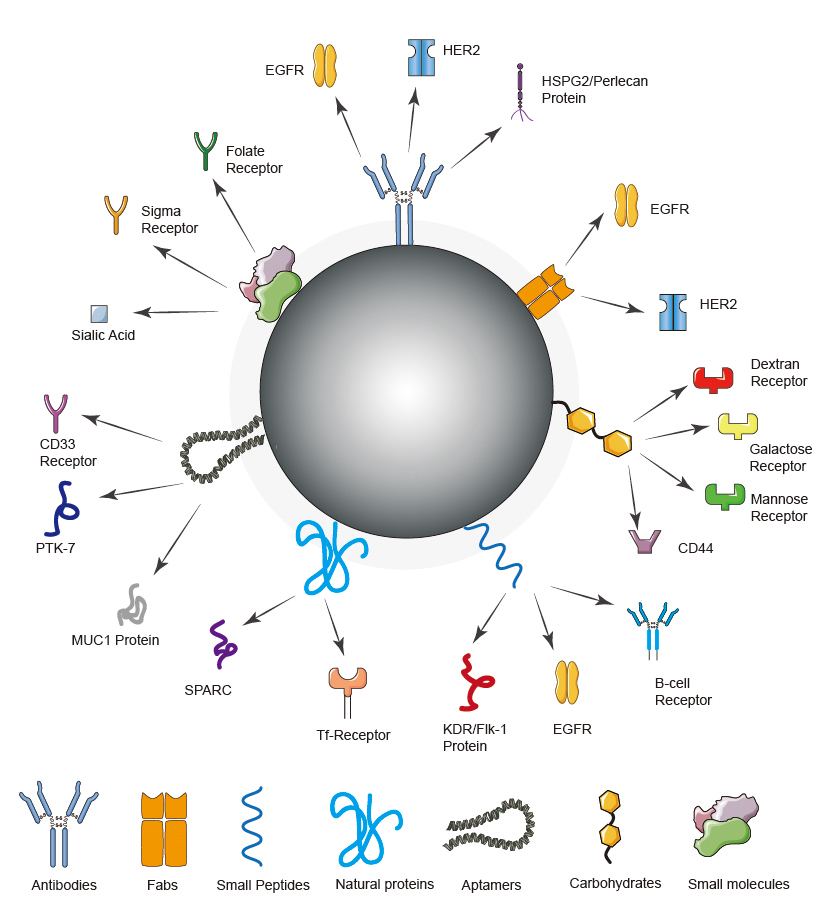 Figure 1. Strategies for targeted delivery of nanoparticles.
Figure 1. Strategies for targeted delivery of nanoparticles.
Key Targeting Ligands Features:
Process of size and structure re-construction discovery
Physical encapsulation discovery
PEGylation discovery
Conjugatable receptor-targeting-moiety discovery
Liposome discovery
Cell-targeting exosome engineering
Virus vector engineering
Protein Toxin engineering
Pro-drug engineering
For more on organ-targeted drug delivery systems, click on here.
Triggered-degradable, conjugation building block discovery
-
Enzyme-responsive degradable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Chemical-responsive degradable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Light-responsive degradable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Electric field responsive degradable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Shear-stress responsive degradable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Temperature responsive degradable nanocarriers and building blocks
Triggered-dissociable micelles, polymersome, nanogel discovery
-
Enzyme-responsive dissociable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Chemical-responsive dissociable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Light-responsive dissociable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Electric field responsive dissociable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Shear-stress responsive dissociable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Temperature responsive dissociable nanocarriers and building blocks
-
Photo-thermal/photo-dynamic/upconversion particle discovery
-
Magnetic particle discovery
Key Targeting Ligands Benefits:
-
The process of size and structure re-construction of the drugs can prolong the circulation time of the drugs
-
Hydrophobic modification of the polar, small drug molecules improves the cell permeability during the passive delivery
-
Hydrolyzable pro-drug prolongs the degradation time to increase the circulation time of the drugs
-
Physical encapsulation systems improve the dispersion and size-regulation of the hardly dissolved drugs
-
Wide coverage of the Antibodies, Aptamers, Affibody, Anticalins, and Adnectins meets your specific cell-membrane-transporter-targeting design
-
Receptor-targeting-moiety modifications increase the uptake rate of the drugs
-
Ready-to-use, reactive-end-group functionalized receptor-targeting-moieties simplifies your preparation procedures for labeling your drugs or your drug-loading cargos
-
Drug-oriented, customized liposome production and formulation improves the delivery efficiency of the drugs, such as nucleic acids, peptides, or molecules
-
Wide coverage of the stimuli-responsive building blocks will be easy for you to develop your ideal controlled delivery system
-
Ready-to-use building blocks and polymer cargo system simplify the preparation of your drug delivery system and promise the reproducibility of your research data
-
GMP promises the quality of products
-
Analytical platforms cover from drug fabrications to in-vitro and in-vivo tests
Drug candidates:
For more information on Nanoparticle Delivery Cargos, click on here.
-
Hardly dissolved, hardly dispersed, crystalized drugs
-
The drugs needed to be further processed, such as dispersion, coating or blending in a new phase
-
Nanoparticles with low targeting efficiency and low targeting specificity
-
Large molecular, peptide or nucleic acid drugs with insufficient cell-permeability
-
Toxic chemotherapeutic agents
-
Nanoparticles with low targeting efficiency and low targeting specificity
-
Programmable delivery
-
Cell specific, or tissue specific targeted delivery conditions
-
Non-invasive therapy or minimally invasive therapy
 Figure 1. Strategies for targeted delivery of nanoparticles.
Figure 1. Strategies for targeted delivery of nanoparticles.