Exosomes are an extracellular vesicle structure with biofilm characteristics secreted by cells of the body. The particle size is 30-150nm. All relevant cells in the body can secrete exosomes of corresponding cell types. Cells with a diameter of 30-150nm External vesicles have a phospholipid bilayer structure and can carry a variety of important biological information such as proteins, nucleic acids (such as miRNA, lncRNA, etc.), lipids, etc. Extracellular vesicles composed of cell membranes (such as exosomes) can attach to target cells through a series of surface adhesion proteins and carrier ligands (tetrapeptides, integrins, CD11b and CD18 receptors) and deliver their payloads to target cells. Some studies have shown that extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes, have specific cellular tropisms depending on their properties and origin and can be used to target diseased tissues or organs. The formation process of exosomes includes the invagination of the cell membrane to form endocytic bodies, the fusion of multiple endosomes into early endosomes, and the early endosomes invaginate again to form multivesicular bodies, which are embedded in the cell membrane. fusion, and finally the formed exosomes are released outside the cell.
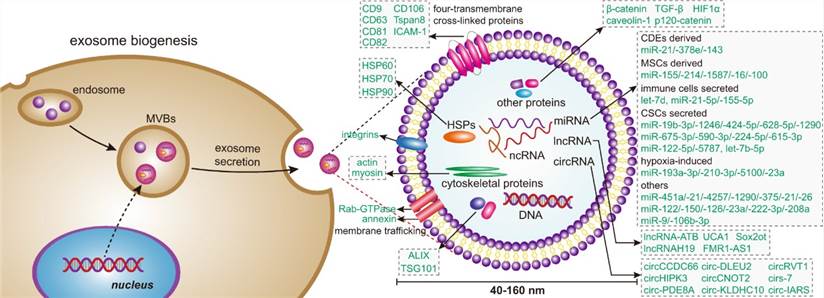 Figure 1. Exosome biogenesis and its contents. (Jie Dai, et al.; 2020)
Figure 1. Exosome biogenesis and its contents. (Jie Dai, et al.; 2020)
Exosomes are derived from endosomes. They are membranous vesicle-like bodies that are released outside the cell after fusion with the plasma membrane through multivesicular bodies (MVBs). There are a variety of biological macromolecules distributed inside, including proteins, nucleic acids, and phospholipids. It has rich biological functions and can serve as an important pathway for intercellular material and signal communication. In the development process of many currently known diseases, exosomes play corresponding roles in participating in various physiological and pathological development processes of the body, and their traces can be seen in all of them. Exosome carriers combine the advantages of cellular drug delivery and nanotechnology. As a new type of drug delivery carrier with natural characteristics, it has the property of crossing the biological barrier of the body. Therefore, using exosomes as a carrier can deliver drugs effectively and safely. It can be delivered to all major systems of the human body, thus becoming a feasible and effective way to treat diseases with excellent prospects.
To this end, CD Bioparticles provides exosome products to help solve the following challenges.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.