Artificial lipid droplets play an important role in the field of drug delivery. It can improve the stability of drugs and increase the bioavailability of drugs. In particular, artificial lipid droplets can achieve specific recognition of the target site and reduce the toxic side effects of drugs on the whole body. Compared with the traditional complex and expensive in vivo pharmacokinetic studies, the establishment of in vitro research models can advance the research progress more rapidly. With the gradual study of lipid droplets, the surface protein composition and lipid composition of lipid droplets have been clarified. The proteins that mediate the interactions between lipid droplets and other organelles have been clarified. However, the isolated and purified lipid droplets in vitro always contained multiple organelle fragments, which caused serious interference in the functional study of lipid droplet proteins. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare artificial lipid droplets with the same structure, similar composition and protein composition as those in vivo, and to establish an in vitro system for the study of lipid droplets. CD Bioparticles can provide lipid droplet models with proteins as organ representatives and in vitro detection of mutual binding strength.
The lipid droplets (LDs) is a cellular organelle that consists of a neutral lipid core with a monolayer-phospholipid membrane and associated proteins. The artificial lipid droplet system can absorb excess fatty acids, remove harmful proteins from the outer mitochondrial membrane, store and transport lipids, and has the same biological functions as endogenous LDs. The establishment of artificial lipid droplets system will provide a new avenue for the functional study of lipid droplet proteins, the interaction of lipid droplets with other organelles and other studies, and will greatly promote the development of the field of lipid droplet biology.
The establishment of artificial lipid droplets is based on two main aspects: the establishment of adiposome and protein recruitment. The key to pure artificial lipid droplet construction lies in the purification of adiposome and LD-associated proteins.
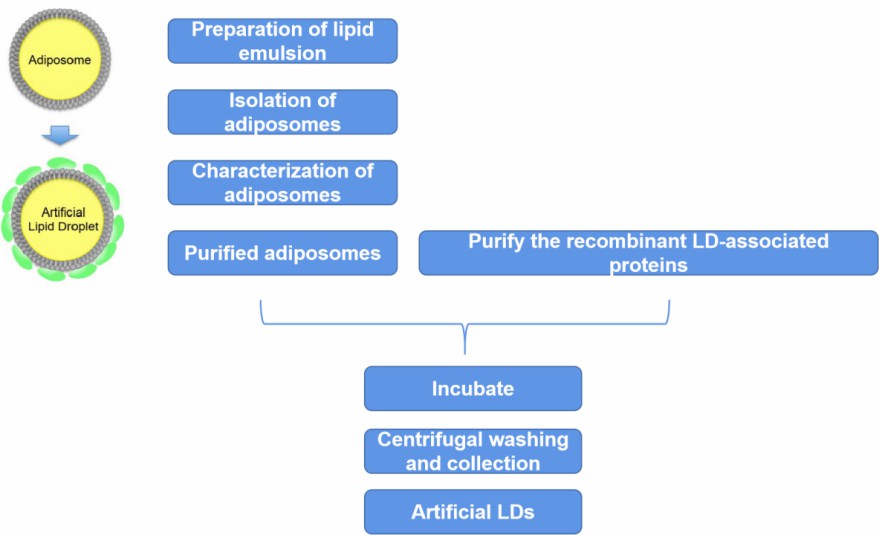 Figure 1. The procedure to prepare artificial LDs[1].
Figure 1. The procedure to prepare artificial LDs[1].
Binding of LD-associated proteins to adiposomes can be saturated and thus follows receptor-ligand binding kinetics. The concentration binding plot is transformed into a linear function using Scatchard analysis.
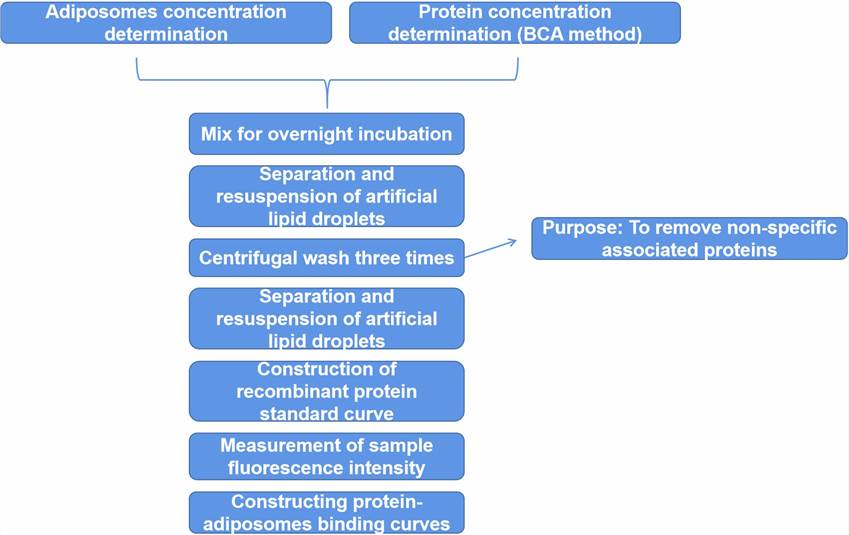 Figure 2. The procedure for protein binding affinity analysis[1].
Figure 2. The procedure for protein binding affinity analysis[1].

Reference
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.