Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors
CD Bioparticles provides adeno-associated virus vectors (AAVs) and a complete AAV expression system, which can be used to express different types of genes in vivo and in vitro, including structural genes, metabolic genes, signal transduction genes to achieve gene replacement, gene silencing, gene addition or gene editing. With the advantages of good stability, reliability reproducibility, high purity and high titer, AAVs can be used to assist you drug development. CD Bioparticles offers comprehensive design, synthesis, and evaluation services. rAAV production steps are showed in Figure 1 below.
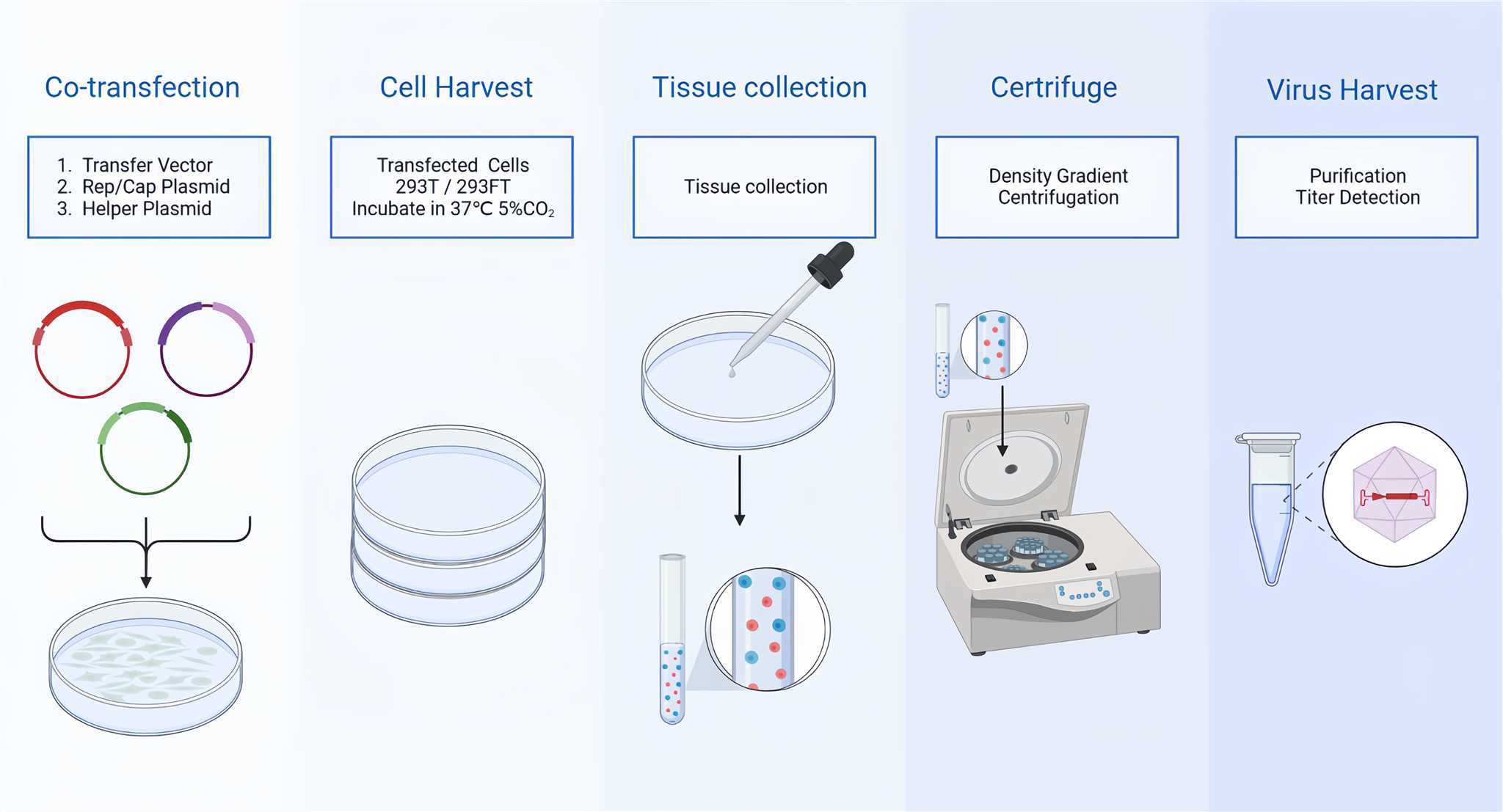 Figure 1. rAAV Production.
Figure 1. rAAV Production.
Introduction to AAVs
The contemporary AAV vector platforms can target diseases on multiple organs, such as the central nervous system, muscles, eyes, heart, and liver. AAVs showed much lower vector-caused cytotoxicity and less immunogenic than adenovirus vectors. Besides the gene therapy application, AAV system is also used for the anti-viral vaccine development. Since the approval of the first AAV-based product, there are more than 200 AAV-based clinical trials being process, holding a lot of promise. Combined with CRISPR/Cas systems, which allow programmed editing nearly anywhere within the genome and have preclinical successes, AAVs show limitless potential.
The Specific Features of AAVs Include:
-
Wide host range: AAV can efficiently infect dividing and non-dividing cells;
-
Multiple serotypes: An overview of wtAAV serotypes and tropism can be found in Table 1;
-
High safety: ITR sequence and rep/cap gene are expressed by independent plasmids; AAV has not been found to be pathogenic to humans, and rAAV has removed 96% of the wtAAV genome, further ensuring safety;
-
Low immunogenicity: The genome of AAV is about 4.7 kb, which is convenient to operate with conventional recombinant DNA technology, and the immune response caused by AAV is weak[1];
-
Long-term expression: AAV can maintain the long-term transcription and expression of genes, and the expression in vivo can reach a peak in 3-4 weeks. Then genes continue to express for more than 5 months. In clinical trials, its expression can even be detected after 2 years.
Table 1 wtAAV serotypes, tropism
|
AAV serotype
|
Preferential tissue tropism
|
|
AAV1
|
skeletal muscle, lung, CNS, retina, pancreas
|
|
AAV2
|
smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, CNS, liver, kidney
|
|
AAV3
|
hepatocarcinoma, skeletal muscle, inner ear
|
|
AAV4
|
hepatocarcinoma, skeletal muscle, inner ear
|
|
AAV5
|
skeletal muscle, CNS, lung, retina, liver
|
|
AAV6
|
skeletal muscle, heart, lung, bone marrow
|
|
AAV7
|
skeletal muscle, retina, CNS
|
|
AAV8
|
liver, skeletal muscle, CNS, retina, pancreas, heart
|
|
AAV9
|
liver, heart, brain, skeletal muscle, lungs, pancreas, kidney
|
|
AAV10
|
liver
|
|
|
CNS, central nervous system
|
The Applications of AAVs Include[2] :
AAVs have a wide range of applications in various fields, and are versatile tools for genetic manipulation, and their applications are continually expanding across different fields, including:
-
Neuroscience: AAVs are used in neuroscience research to study the functioning of specific neurons in the brain.
-
Immunology: AAVs are used to deliver therapeutic genes to the immune system for treating autoimmune disorders.
-
Cancer therapy: AAVs are being studied for their potential to deliver gene therapies for treating various types of cancer.
-
Agriculture: AAVs are used to modify crops and animals for improved yield, disease resistance, and other traits.
-
Biotechnology: AAVs are used in biotechnology for protein production and gene editing.
Our AAVs Featured Services:
-
AAV packaging service:
-
ssRNA and scRNA: AAV packaging services with ssRNA or scRNA genomes. Gene expression by scRNA is faster and the ssRNA gene load is larger;
-
Multiple AAV serotypes: According to different experimental designs, we are constantly mutating to produce novel serotypes. Currently we have AAV serotypes (AAV1-13, AAV2/1, 2/2, 2/5, 2/6, 2/8, 2/9, DJ; retro, PHP. eB…);
-
Multiple vectors: different promoters (CAG/CBG, CamkIIα, GFAP, cTNT, etc.) and a variety of reporter genes (EGFP, mCherry, RFP, luciferase, etc.) are available for customers to choose;
-
High titer: High titer of viral particles, >1010 GC/ml, up to 1013 GC/ml.
-
AAV control particles: Use empty vectors as controls for your experiments.
-
Directed evolution of AAV capsids: AAV capsid directed evolution obtains a highly diverse AAV capsid library by mutating the wild-type AAV capsid gene, and then screens out a new AAV capsid with better performance.
-
Testing in vitro and in vivo: localization studies, infection rate, gene expression assessment, immunogenicity assessment, in vivo distribution, in vivo metabolism, off-target evaluation, toxicological evaluation, etc.
We are committed to providing you with excellent services and products. Please contact us if you have questions.
Quotations and Ordering

References
-
Yang T-y, Braun M; et al. Immunogenicity assessment of AAV-based gene therapies: An IQ consortium industry white paper. Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development. 2022, 26:471-494.
-
Bulcha JT, Wang Y; et al. Viral vector platforms within the gene therapy landscape. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021, 6(1):53.
 Figure 1. rAAV Production.
Figure 1. rAAV Production.
