Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a key intermediate in the synthesis of coenzyme I (NAD+). NMN serves as a precursor to NAD+ and can be supplemented to increase NAD+ levels in the body. Studies have shown that NMN supplementation can increase NAD+ concentrations and may attenuate aging-related diseases such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, neurodegenerative and inflammatory responses. NMN supplementation has shown positive effects in animal models, including slowing aging and preventing age-related diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, diabetes and metabolic dysfunction. However, NMN is susceptible to deterioration due to temperature and humidity, and liposomes are well suited to address this challenge.
This encapsulation property of liposomes makes them an effective drug delivery system that can improve drug stability and bioavailability while reducing toxic side effects and enabling targeted delivery. CD Bioparticles has extensive experience in developing liposomes over the years and has the capability for stable batch production and industrialization. Liposomal NMN prepared using high-pressure homogenization technology exhibit the following properties:
| NMN Content | Phospholipid Content | Phospholipids | Encapsulation Rate | Particle Size (DLS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30% | 40-50% | Sunflower Phospholipid (P2) | 20-40% | 50 nm |
Note: P2 is a special process formulation 1. P6 is a special process formulation 2.
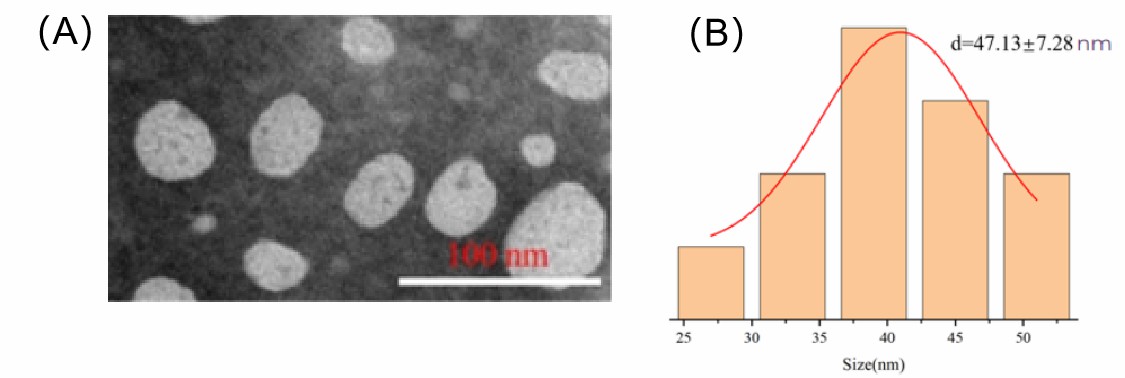 Figure 1. (A) TEM picture of liposomal NMN; (B) DLS of liposomal NMN.
Figure 1. (A) TEM picture of liposomal NMN; (B) DLS of liposomal NMN.
 Figure 2. Pictures of NAD+ levels in mouse liver and skeletal muscle.
Figure 2. Pictures of NAD+ levels in mouse liver and skeletal muscle.

References
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.
1. Download the template.
2. Enter product information on the template (maximum number of products: 200).
3. Load the file using selector below.