Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are ordered and porous networks through the connection of metal ions or clusters with organic molecules. Scientists study MOFs because these materials offer many advantages like structural flexibility and large surface area plus their ability to store gases, speed up chemical reactions and deliver medicine. Among all MOF types MOF-177 leads in drug delivery research because of its effective qualities.
Introduction MOF-177
Researchers widely study MOF-177 as a Metal-Organic Framework with extraordinary porosity and structural durability. Zinc ions (Zn²⁺) and benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate (BTC) organic linkers work together to form the MOF-177 framework structure. The material's open crystal network lets it serve effectively in systems requiring extensive surface space and controlled pore dimensions. Scientists and researchers often mention MOF-177 in studies about gas storage and environmental uses because it can absorb substances effectively.
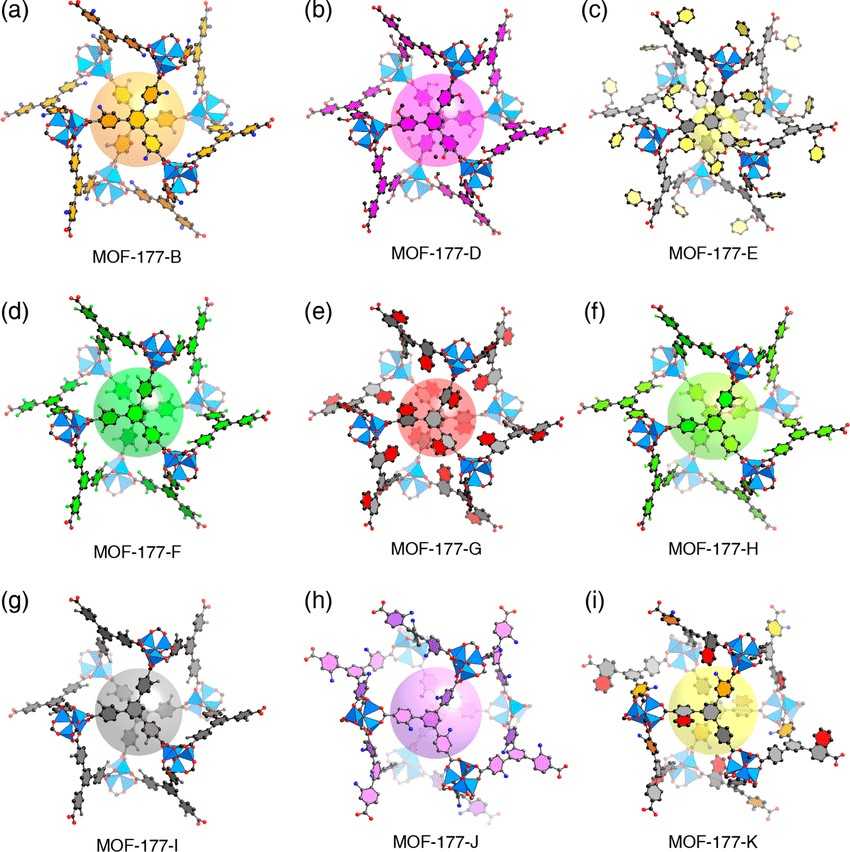 Figure 1. Crystal structures of MOF-177 compounds synthesized from linkers with various functional groups. (Zhang YB, et al.; 2015)
Figure 1. Crystal structures of MOF-177 compounds synthesized from linkers with various functional groups. (Zhang YB, et al.; 2015)
MOF-177 stands out because its distinct pore structure creates an enormous surface area that lets molecules such as gases liquids and biomolecules attach better. MOF-177 stands out as a great drug delivery material because its high surface area and adjustable surface features work well together.
The Crystal Structure of MOF-177
The zinc ions in MOF-177 form a three-dimensional network with BTC organic ligands. The metal-ligand bonds in MOF-177 form a cubic structure that contains open spaces connected across the entire framework. MOF-177 works best because its internal pores let molecules move in and out without restriction. MOF-177 framework design achieves maximum surface area without compromising material stability over different conditions.
The zinc ions connect with BTC linkers to create a truncated octahedral shape where each zinc ion links to multiple BTC units. The arrangement creates numerous connected pores in MOF-177 that offer ideal gas storage and molecular separation conditions.
The distinct atomic arrangement of MOF-177 framework determines its applications because scientists can modify its structure to create functional solutions. Through changes to the organic linkers and metal nodes researchers can customize the MOF-177 material's internal structure and surface composition for precise molecule interactions. MOF-177's multiple uses in drug delivery benefit from its customizable pore design for drug transport and release.
The Pore Size of MOF-177
The precise measurement of MOF-177 pores defines how well this material works in its different uses. The pores of MOF-177 generally measure between 1 and 3 nanometers to create mesoporous spaces that can trap numerous molecular types. The pores in MOF-177 framework measure large enough for small molecules like drugs to enter but small enough to keep out bigger macromolecules. The mesoporous design of MOF-177 creates a surface area above 3000 m²/g that enables superior storage and release of molecules.
The size of MOF-177 pores defines when drugs inside escape from the delivery system. Scientists achieve precise drug release patterns by using MOF-177 with pores that accept small drug molecules. The numerous pores in MOF-177 create a large area for drugs to occupy so they can be effectively loaded into small volumes.
Our researchers can modify the pore size of this structure to match the size of particular drugs and even deliver medication precisely to specific areas of the body. The specific filtering abilities of these pores help doctors deliver medicine precisely to the desired parts of the body such as tumors.
MOF-177 Synthesis
To create MOF-177 you mix zinc salts and organic linkers in a controlled environment. Scientists typically use the solvothermal method to create MOF-177 by combining zinc nitrate and BTC in dimethylformamide (DMF) before heating under high pressure. The created MOF structure becomes ready for purification through washing and drying steps.
Developing MOF-177 requires controlling how the framework forms its crystals and their dimensions. The solvothermal method needs exact temperature and timing controls to create MOF with specific features. The synthesis method depends heavily on the right amounts of metal salt and organic linker plus the selection of proper solvent. Even minor adjustments to synthetic conditions impact how the finished product looks and how much air it contains.
Hydrothermal synthesis works differently to make MOF-177 by using water instead of other solvents under carefully controlled conditions. Hydrothermal synthesis provides an eco-friendly option though it produces MOF-177 crystals with lower quality compared to solvothermal processes but shows promise for industrial-scale production.
After making MOF-177 the material requires XRD, SEM, and nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms for examination. These analysis methods prove that MOF-177 material forms regular crystals while showing its surface area characteristics and revealing its inner structure details.
Drug Delivery System of MOF-177
Researchers see MOF-177 as an excellent choice for creating drug delivery systems. MOF-177 shows drug delivery potential because its open structure offers many absorption sites and its customizable features make it good at releasing medications at planned times. MOF-177 can store many types of drugs because its porous structure lets scientists design specific openings and surface features.
Researcher uses MOF-177 for drug delivery systems because they design this material to release medications precisely at targeted regions of the human body. MOF-177 shows better treatment results when combined with specific targeting molecules because these molecules help the material find and attach to cancer cells during therapy.
MOF-177 works well as a drug carrier because it releases medicine slowly over time. MOF-177's porous design lets drugs exit slowly from its hollow spaces which produces better drug release control than regular methods. MOF-177 releases drugs slowly which helps cancer treatments work better by keeping steady drug levels at the tumor area.
MOF-177 demonstrates successful drug delivery by releasing multiple drugs that work together to treat patients. Multiple treatments are needed for cancer therapy to work because each drug attacks separate pathways that support tumor development and spread.
The drug delivery possibilities of MOF-177 stand out but research needs to address key issues first. Researchers need to examine how well MOF-177 fits with living tissues and how dangerous it might be before doctors can use it in medical care. Researchers study ways to make MOF-177 last longer while breaking down faster plus design better drug release patterns for medical treatments.
Conclusion
MOF-177 shows potential as an exceptional material with many advantages that make it valuable for multiple applications especially drug delivery systems. The material's open network design with adjustable pores and great surface area helps it hold therapeutic agents well and release them effectively. The substance can be adjusted to create special drug delivery systems that release medicine exactly when and where it's needed.
Research on MOF-177 development will unlock additional applications in drug delivery plus catalysis and gas storage. MOF-177 proves essential in drug delivery research because of its special characteristics which help create better next-generation medicine.
MOF-177 stands out as a remarkable material with promising prospects for drug delivery systems which can enhance medical therapy across many healthcare fields.
References
- Zhang YB, et al.; Introduction of functionality, selection of topology, and enhancement of gas adsorption in multivariate metal-organic framework-177. J Am Chem Soc. 2015, 137(7):2641-50.
- Wu MX, Yang YW. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Drug/Cargo Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Adv Mater. 2017, 29(23).


 Figure 1. Crystal structures of MOF-177 compounds synthesized from linkers with various functional groups. (Zhang YB, et al.; 2015)
Figure 1. Crystal structures of MOF-177 compounds synthesized from linkers with various functional groups. (Zhang YB, et al.; 2015)